Advancements in Rapid Prototyping Materials and Technologies
Understanding Rapid Prototyping Technologies
Rapid prototyping is a pivotal technology in design and manufacturing, significantly reducing time-to-market and enhancing product design through fast iterations and testing. It allows designers to quickly produce physical prototypes from digital designs, facilitating prompt feedback and design refinement. This acceleration not only speeds up the product development process but also improves the final design by enabling multiple rounds of testing and iterative enhancements. For industries like automotive and consumer electronics, this means quicker adaptions and more tailored products hitting the market faster, ultimately fostering innovation and competitiveness.
Materials used in rapid prototyping vary widely and are chosen based on their properties and application needs. Common materials include polymers, metals, and composites. Polymers are often used for their flexibility and low cost, making them suitable for initial concept models. Metals like aluminum or stainless steel provide durability and strength, ideal for functional testing. Composites, offering a balance of weight and strength, are often used in aerospace and automotive parts manufacturing where performance is critical. These diverse material options allow for customized prototypes that align with specific industry requirements and applications.
Several key technologies underpin rapid prototyping. Stereolithography (SLA) uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid structures layer by layer, ideal for high-precision models. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is another method, where a thermoplastic filament is melted and extruded to form objects, commonly used due to its affordability and simplicity. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) employs a laser to sinter powdered material, typically plastic or metal, providing strong parts for functional prototypes. Each of these technologies offers distinct benefits, making them suitable for different materials and design complexities, thus broadening the range of applications in modern manufacturing.
Advancements in Additive Manufacturing for Rapid Prototyping
Advancements in additive manufacturing are transforming rapid prototyping by introducing innovative materials such as bio-materials, nano-composites, and high-performance plastics. These materials are gaining popularity due to their versatility and enhanced properties. Studies indicate that bio-materials are increasingly used in applications requiring biocompatibility and environmental sustainability, while nano-composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios. High-performance plastics are also making waves in industries that demand greater thermal and chemical resistance, thus broadening the scope of rapid prototyping across various fields.
Moreover, revolutionary 3D printing techniques are pushing the boundaries of what's possible in rapid prototyping. Multi-material printing allows for the combination of different materials in a single print, leading to more complex and functional prototypes. The Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) technique stands out by drastically reducing print times and improving surface finishes. Additionally, integrating Artificial Intelligence in the design process is being spearheaded by companies like Carbon3D and Formlabs. These advancements not only enhance design flexibility but also streamline the prototyping process, catering to the demands of industries such as automotive parts manufacturing and sheet metal fabrication services.
Impact of Rapid Prototyping on Industries
Rapid prototyping plays a crucial role in enhancing automotive parts manufacturing. This technology allows automakers to drastically reduce development times and improve efficiency, as evident in notable case studies. For example, Volkswagen has incorporated rapid prototyping to create 3D printed tools, which reduced their purchasing costs by 91% and implementation time by 95%. This transformation in production processes not only accelerates the design phase but also supports sheet metal fabrication and the customization of prototype vehicles to meet specific consumer needs.
In the healthcare and aerospace sectors, rapid prototyping has enabled significant advancements. In healthcare, the technology facilitates the creation of custom implants and medical devices tailored to individual patient anatomies, thereby enhancing treatment outcomes. Aerospace companies utilize rapid prototyping to fabricate lightweight and complex components for aircraft. This use in manufacturing aircraft parts contributes to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, as parts can be designed with intricate geometries unachievable through conventional methods. These industries benefit from rapid prototyping technologies that offer customization, precision, and efficiency, positioning them for ongoing innovation.
Challenges and Considerations in Rapid Prototyping
When engaging in rapid prototyping, material limitations are a significant challenge. Materials often used in prototyping, such as thermoplastics and resins, may not always offer the strength and durability required for certain applications, particularly in fields like aerospace and healthcare where biocompatibility and environmental factors are of utmost concern. The selection of appropriate materials that can withstand the required operational conditions is crucial, yet it remains a complex barrier due to varying requirements across different industries.
In addition to material constraints, the cost implications and production scalability of rapid prototyping are critical considerations. While rapid prototyping can potentially reduce initial costs by avoiding extensive tooling expenditures, scaling from prototypes to full production involves additional costs that need careful assessment. Companies need to find a balance between the low costs associated with rapid prototyping and the need for high-quality outputs. This often involves investing in advanced technologies and maintaining a strategic approach to manage production resources effectively to ensure that the prototype not only meets quality standards but is also feasible for larger scale production.
Products and Technologies in Rapid Prototyping
Factory vacuum casting is a highly effective method used in the realm of rapid prototyping for plastic products. This technique is particularly appreciated for its speed and cost-efficiency, making it an ideal choice for manufacturers aiming to bring new products to market quickly. Vacuum casting allows for the rapid production of high-quality prototypes, crucial for testing and finalizing product designs before mass production.
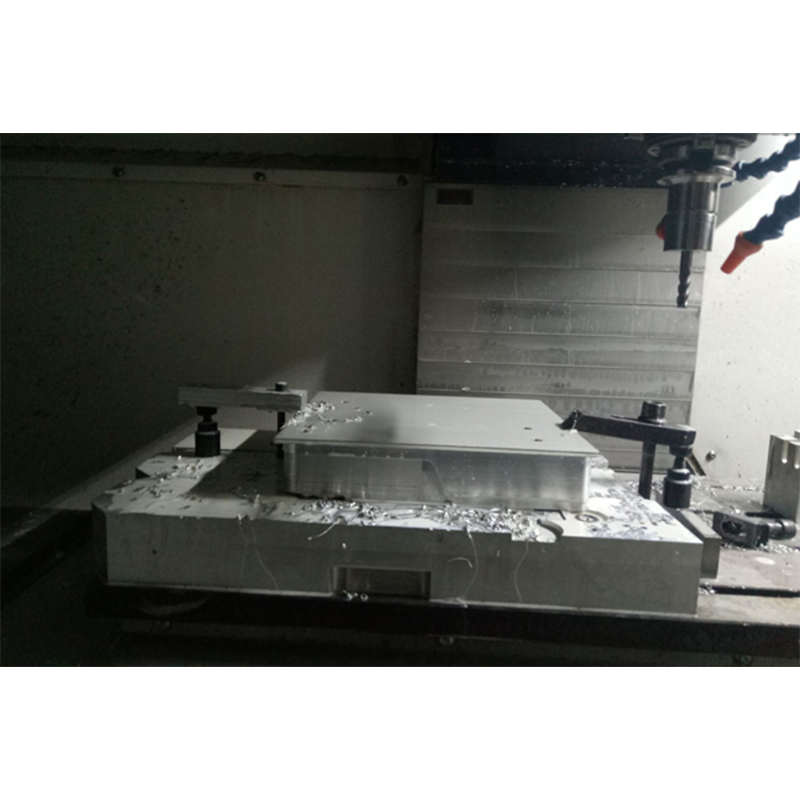
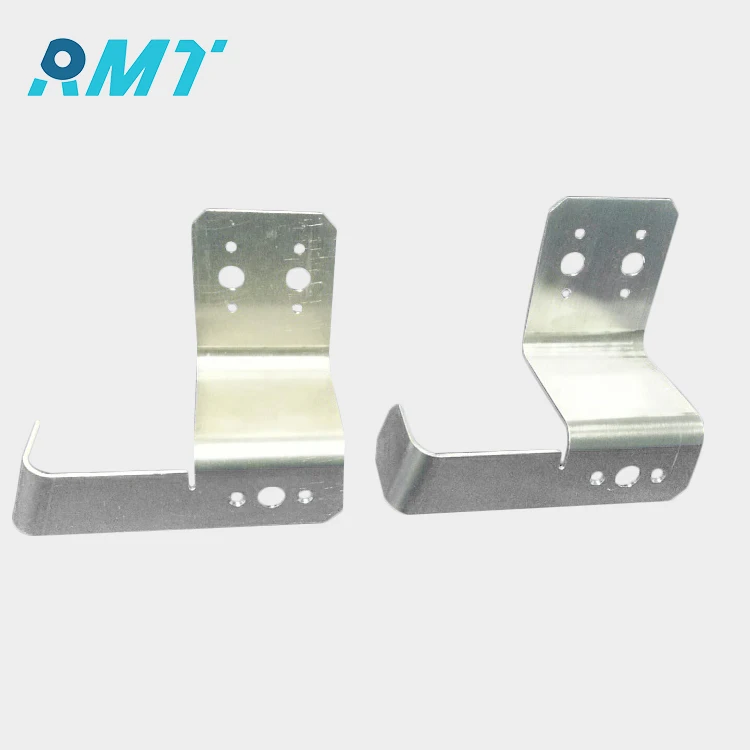
Furthermore, rapid prototyping is significantly enhanced by technologies such as CNC machining and sheet metal fabrication. CNC machining offers precise control over product dimensions, which is essential for developing accurate models in prototyping phases. Meanwhile, sheet metal fabrication allows for the creation of robust prototypes, suitable for products where metal strength is crucial. Both technologies are integral to enhancing the speed and accuracy of the prototyping process, thus enabling companies to iterate and refine their products efficiently.
The Future of Rapid Prototyping Technologies
The future of rapid prototyping technologies is driven by several key trends and potential innovations. Emerging trends include the adoption of sustainable practices and the integration of advanced robotics and automation. These advancements promise to streamline prototyping processes and increase precision. Furthermore, innovations in materials, such as self-healing and more biocompatible options, are attracting significant attention. Researchers speculate that these materials will play crucial roles in enhancing product development, as they allow for more complex designs and applications in fields like healthcare and automotive parts manufacturing.
As rapid prototyping continues to evolve, advancements in CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and rapid prototyping will be critical in meeting future demands. Industry experts suggest that these technologies will not only improve manufacturing efficiency but also enhance the quality and customization of prototypes. As a result, businesses can expect to see a more seamless transition from design to production, ultimately accelerating innovation across various sectors.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 LV
LV
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 EU
EU
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 LA
LA
 NE
NE
 SO
SO
 KK
KK












