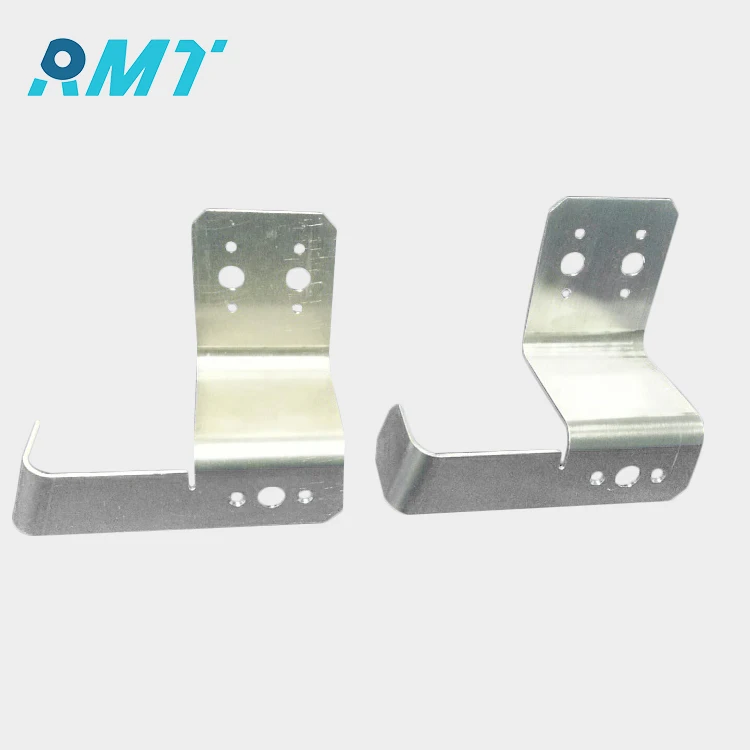
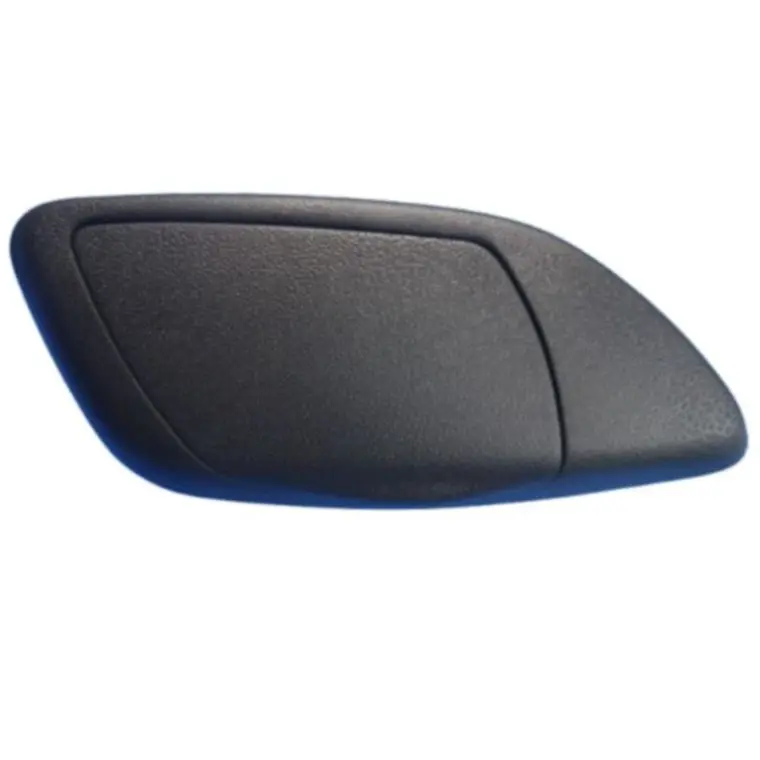
Sheet Metal Components: The Backbone of Modern Manufacturing
In the vast landscape of manufacturing, sheet metal components stand as pivotal elements in the construction of a myriad of products. These components, often overlooked, are integral to the structural integrity and functionality of everything from household appliances to aerospace technology.
Understanding Sheet Metal Components
Sheet metal components are fabricated from thin sheets of metal that are typically less than 6 mm in thickness. The versatility of these components lies in their ability to be cut, bent, and shaped into various forms through processes like stamping, bending, and cutting. The choice of material—be it steel, aluminum, copper, or brass—depends on the required strength, conductivity, or corrosion resistance for the end product.
The Manufacturing Process
The journey of a sheet metal component begins with design precision. Engineers use CAD software to draft the initial designs, ensuring each measurement is accurate to the millimeter. Following design, the manufacturing process involves several stages, including cutting, punching, bending, and assembling. Advanced machinery, such as CNC machines, laser cutters, and press brakes, are employed to achieve the desired shapes with high precision.
Innovation in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Innovation in sheet metal fabrication is driven by the need for efficiency and sustainability. Techniques like hydroforming and 3D printing are revolutionizing the industry, allowing for more complex shapes and reducing waste. Additionally, the use of robotics and automation in sheet metal fabrication has increased production speeds and consistency while minimizing human error.
Applications in Various Industries
Sheet metal components are ubiquitous across industries. In the automotive sector, they form the exoskeleton of vehicles, providing both aesthetic appeal and crash protection. In electronics, they are used to create enclosures for devices, aiding in heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding. The construction industry relies on sheet metal for roofing, siding, and HVAC systems, while aerospace applications include fuselage and wing structures.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite their widespread use, the production of sheet metal components is not without challenges. The rising cost of raw materials and the need for skilled labor are ongoing concerns. Moreover, the push for greener manufacturing practices is prompting the industry to explore recycling and material reusability.
The future of sheet metal components is bright, with ongoing research into new alloys and composite materials that promise lighter, stronger, and more durable products. As technology advances, so too will the capabilities of sheet metal fabrication, ensuring that these components continue to play a crucial role in the manufacturing world.
Conclusion
Sheet metal components may not always be visible in the final product, but their presence is essential. They provide the structural foundation upon which innovation builds. As we continue to push the boundaries of what's possible, sheet metal components will undoubtedly remain at the heart of manufacturing, silently supporting the creations that move us forward.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 LV
LV
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 EU
EU
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 LA
LA
 NE
NE
 SO
SO
 KK
KK











